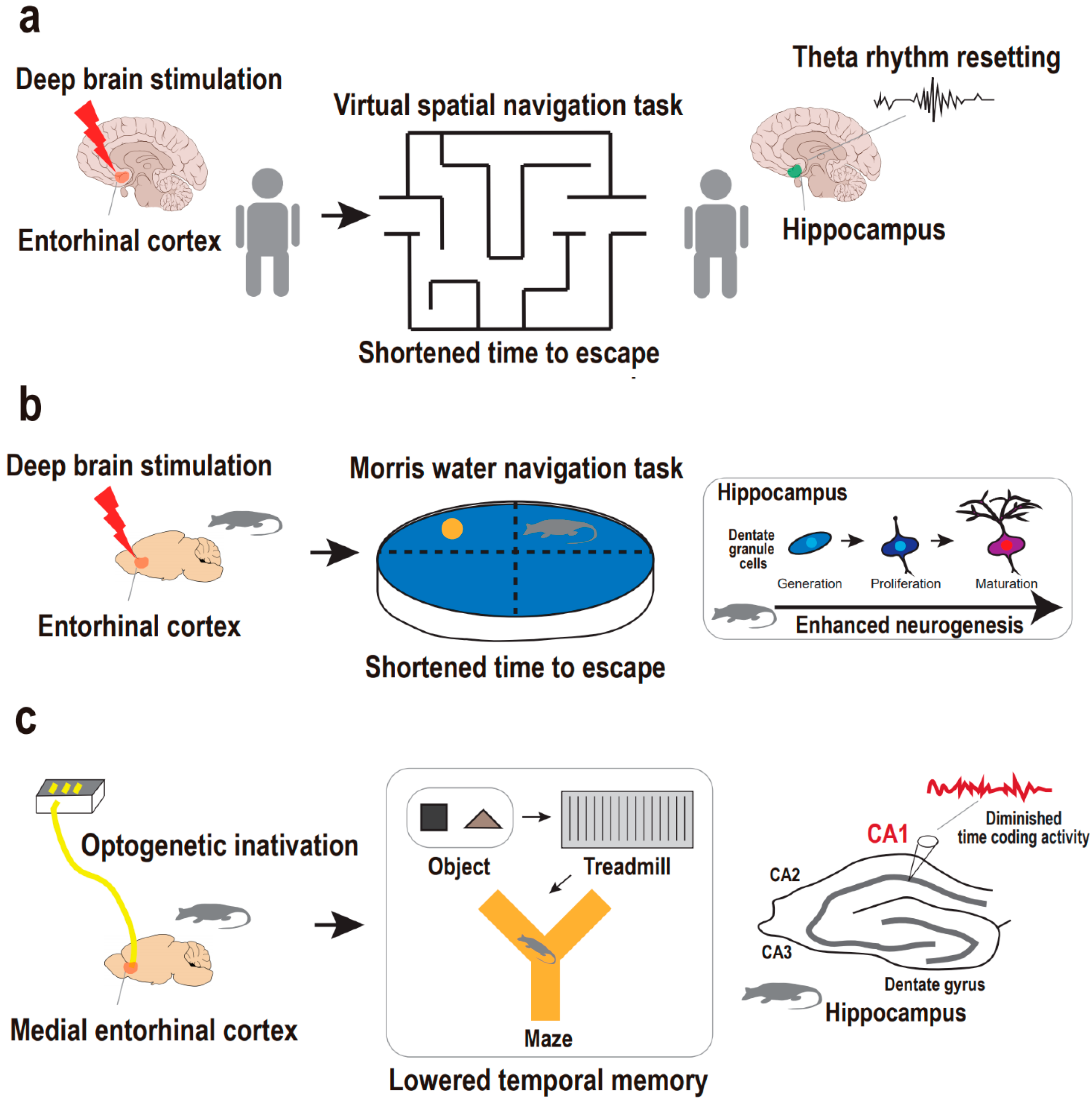
Recently neural plasticity theories of depression have postulated that multiple aspects of brain plasticity beyond neurogenesis may bridge the prevailing theories. This research strongly suggests that the most effective treatments for severe depression Prozac and ECT work by increasing the rate of neurogenesis in the hippocampus.
Ijms Free Full Text Neural Circuitry Neurogenesis Coupling Model Of Depression Html
Data from the animal models tested to date show that decreasing the rate of neurogenesis does not lead to depressive behavior.

. Beside this potential the function of newly generated neuronal cells in the adult brain remains th. Researchers have turned their focus to chemicals in the brain that promote neurogenesis and suggest that new treatments targeting said chemicals could be a more logical and effective treatment for. All of the above.
Within each adult human hippocampal dentate gyrus approximately 700 newborn granule cells are added daily 1. C It is unrelated to health emotion regulation and social functioning. The observations that antidepressants like fl uoxetine increase.
These findings extend our understanding of the contribution of adult neurogenesis to anxiety and depression and suggest that neurogenesis may be harnessed to develop novel antidepressants. A neurogenic hypothesis of depression has been postulated which suggests that reduced adult hippocampal neurogenesis may underlie the pathoetiology of depression while antidepressant efficacy depends on the upregulation of hippocampal neurogenesis. Something else we know is that it doesnt take place nearly as much in people who suffer from depression symptoms.
There is growing evidence that stress causes a decrease of neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus and antidepressant treatment in turn stimulates the cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus. This suggests that adult neurogenesis may contribute to the biology of depression. In support of this contention gluco-corticoids stress-related hormones induce brain atrophy Sapolsky 2000.
What does the neurogenesis theory of depression suggest. Several lines of evidence suggest that adult neurogenesis the production of new neurons in adulthood may play a role in psychiatric disorders including depression anxiety and. A prerequisite for effective control of depression and related mood disorders is to understand their detailed molecular pathways.
First formally proposed in 2000 the neurogenic theory of depression posits that impaired adult hippocampal neurogenesis AHN triggers depression and restoration of AHN leads to recovery 2. Several studies have found that people who suffer from major depression for several months actually have measurable smaller hippocampus regions. C 50 to 60 times.
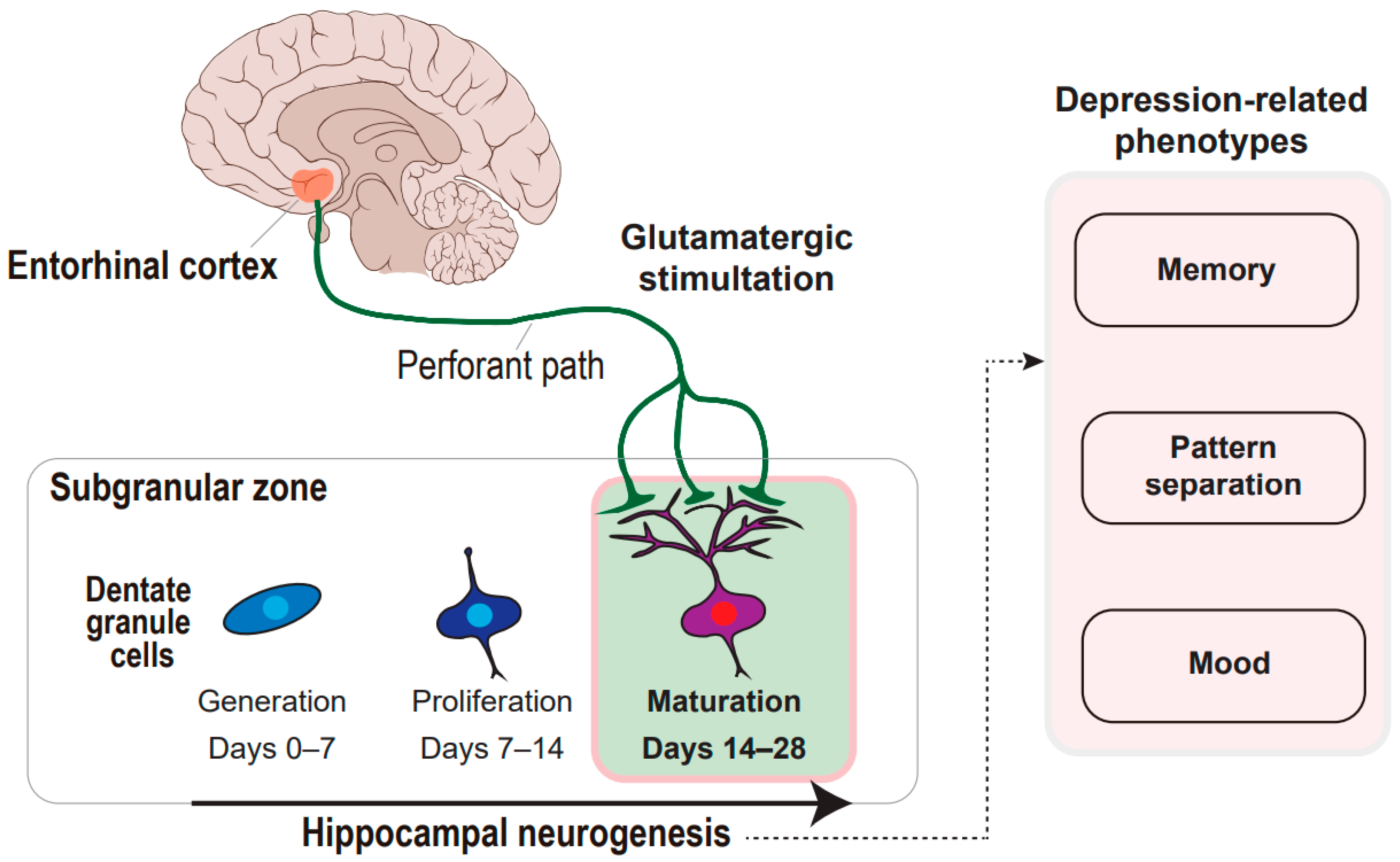
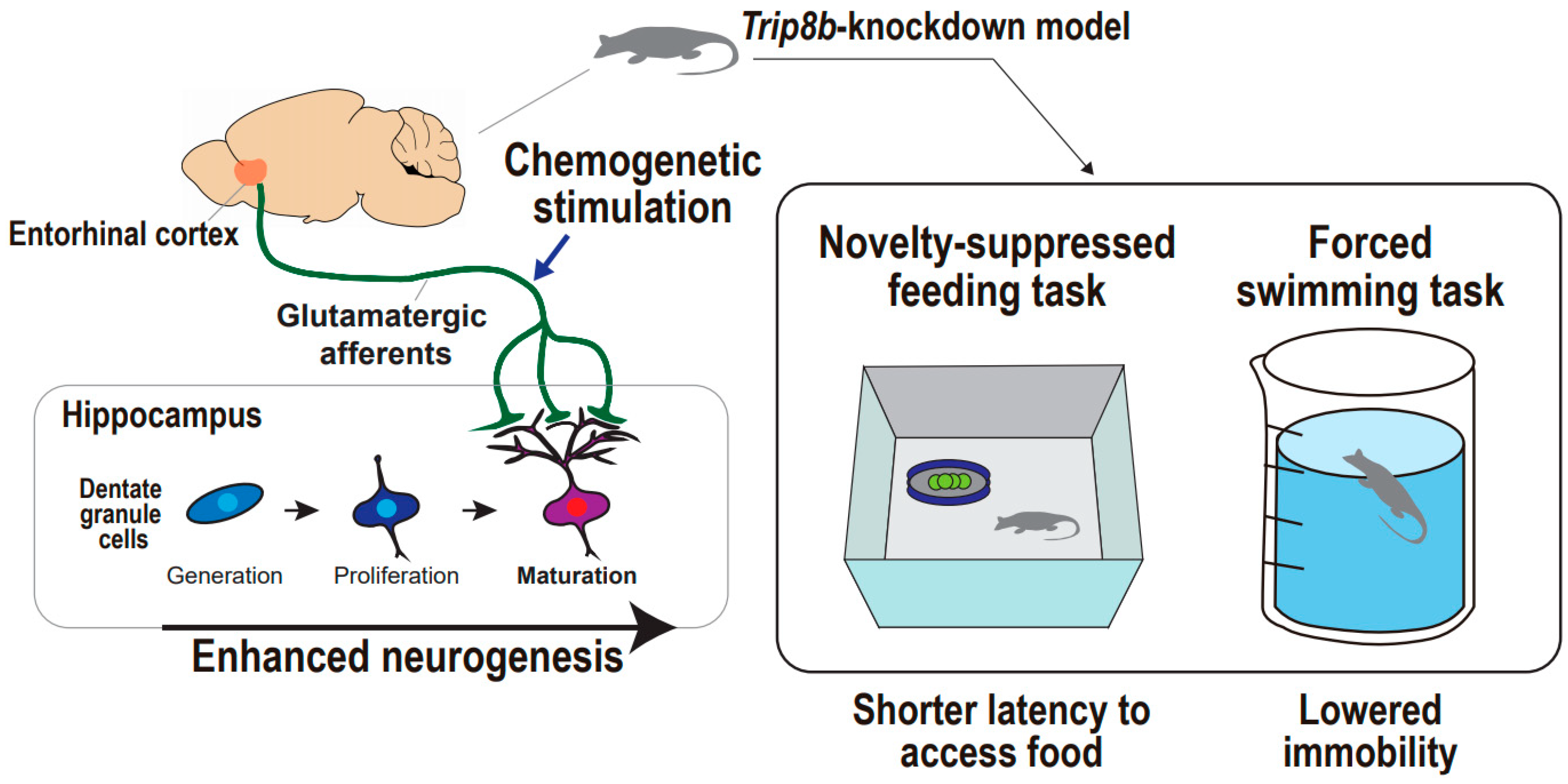
Recent research suggests that the suppression of neurogenesis in the hippocampus is due to the connection between high stress hormones and depression. The recent evidence that neurogenesis occurs throughout adulthood and neural stem cells NSCs reside in the adult central nervous system CNS suggests that the CNS has the potential for self-repair. This has led to the hypothesis that a decreased neurogenesis might be linked to the pathophysiology of major depression.
Follow up studies yielded a complex body of often inconsistent results and the veracity of this theory is. Low hippocampal volume may precede and contribute to the onset of depression. Specifically researchers have focused on neurogenesis in the hippocampus one of the only areas in the brain where neurogenesis has been observed in adulthood the other being the.
Cameron and Gould 1994 whereas antidepressants like. The neurogenic theory suggests that impaired neurogenesis within the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus is one of the factors causing depression. A 75 to 80 times.
This suggests that neurogenesis may be an under-lying factor in the contribution of the hippocampus to depression. This led to the theory that depression results from impaired adult neurogenesis and restoration of adult neurogenesis leads to recovery. What we do know is that neurogenesis takes place.
Immunology also has an impact on neurotrophic factors. The recent evidence that neurogenesis occurs throughout adulthood and neural stem cells NSCs reside in the adult central nervous system CNS. The neurogenesis theory of depression explains that the delay in mood improvement is a result of the minimal effect serotonin has on neurogenesis.
The aim of the study was to assess the importance of selected genes involved in the p. Electroconvulsive therapy seems to produce neurogenesis in the hippocampus. The concept that decreased neurogenesis might be the cause of depression is supported by the effects of stress on neurogenesis and the demonstration that neurogenesis seems to be necessary for antidepressant action.
This suggests that adult neurogenesis may contribute to the biology of. D According to the cellular clock theory of aging cells can divide a maximum of. The neurogenesis hypothesis of depression posits 1 that neurogenesis in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus is regulated negatively by stressful experiences and positively by treatment with antidepressant drugs and 2 that alterations in the rate of neurogenesis play a fundamental role in the pathology and treatment of major depression.
Although the classical stress model of depression and current understanding of antidepressant action appears to be partially linked via epigenetic mechanisms and hippocampal neurogenesis Figure 1 obviously the current picture of the. The neurogenic hypothesis suggests that depression is at least partially caused by an impairment of the brains ability to produce new neurons a process known as neurogenesis. The observations that antidepressants like fluoxetine increase neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus DG and neurogenesis is required for the behavioral effect of antidepressants lead to a new theory for depression and the design of new strategies and drugs for the treatment of.
The neurogenesis hypothesis of depression posits 1 that neurogenesis in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus is regulated negatively by stressful experiences and positively by treatment with antidepressant drugs and 2 that alterations in the rate of neurogenesis play a fundamental role in the pathology and. D It involves managing ones thoughts to engage in goal-directed behavior and to exercise self-control. McEwen 2001 and decrease neurogenesis Gould et al.
B 80 to 100 times. Early studies found that adult neurogenesis is impaired in models of depression and anxiety and accelerated by antidepressant treatment. He term neural plasticity encompasses an array of mechanisms from the birth survival migration and integration of new neurons to neurite outgrowth synaptogenesis and the modulation of mature synapses.
Ijms Free Full Text Neural Circuitry Neurogenesis Coupling Model Of Depression Html
Ijms Free Full Text Neural Circuitry Neurogenesis Coupling Model Of Depression Html
0 Comments